Stakeholder
Success Stories
Maine Department of Environmental Protection
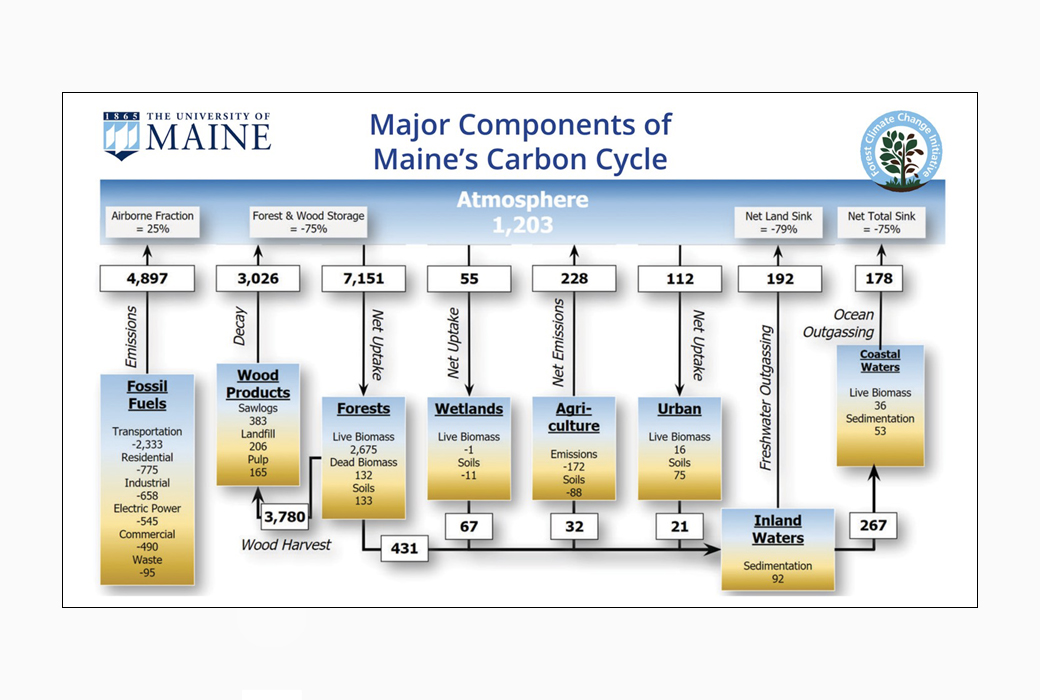
The state of Maine has set ambitious greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions reduction goals as a core strategy for its climate action plan, “Maine Won’t Wait”. In 2019, the state established statutory mitigation targets requiring a 45% reduction in gross GHG emissions below 1990 levels by 2030, and at least 80% reduction by 2050. A critical part of this process is the tracking and biennial reporting of progress toward these goals by the Maine Department of Environmental Protection (DEP). These goals were expanded by a 2022 executive order that added a target for achieving carbon neutrality in the state by 2045. Monitoring progress toward carbon neutrality now requires the DEP, in addition to reporting gross GHG emissions, to also quantify net emissions by accounting for carbon sequestration in the environment.
While DEP has well-established methods for calculating gross emissions from the energy sector, there is now a need to acquire the data and develop the protocols to calculate net emissions from the natural and working lands in Maine. This need led to a partnership between DEP and NASA CMS science team investigators from the University of Maine in undertaking an effort to synthesize various sources of inventory, remote sensing, and model data to estimate carbon stocks and fluxes in the forestry sector, along with other components of the statewide budget. This work made it possible, for the first time, to include the net emissions calculation in tracking the state’s progress toward its climate goals. The most recent Ninth Biennial Report on Progress toward Greenhouse Gas Reduction Goals (July 2022) showed that approximately 75% of gross GHG emissions in the state were offset by sequestration in the forestland and wood products carbon pools.
The primary stakeholder partner in this effort, Stacy Knapp (inventory manager for the Bureau of Air Quality, Maine DEP) gave an invited virtual presentation for the Multi-State Working Group meeting (organized by CMS science team lead and PI George Hurtt) in March 2023. She also attended the CMS Science Team meeting in September 2023 in Pasadena, CA, participating as a panelist on an important discussion highlighting the applications of CMS data products with examples of successful stakeholder engagement activities. The University of Maine CMS project investigators continue to work closely with the DEP on this on-going effort, which is currently getting ready to release the next iteration of the Maine Carbon Budget assessment to be included in the upcoming Tenth Biennial Report.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency
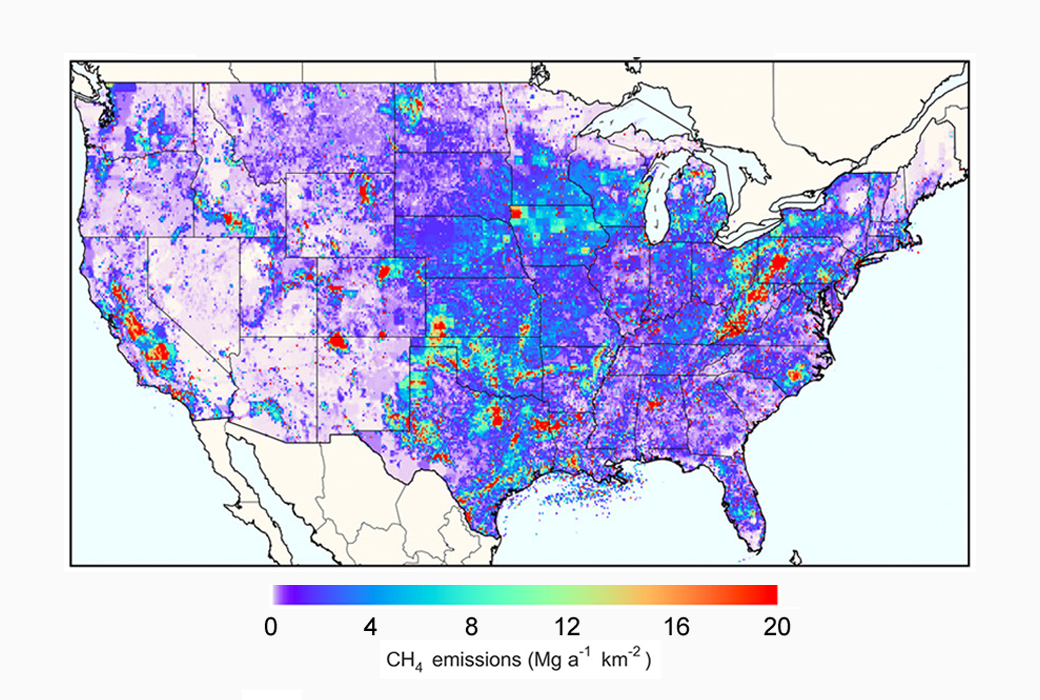
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is using the Gridded National Inventory of U.S. Methane Emissions, a dataset developed by CMS Principal Investigator Daniel Jacob and his team at Harvard University. The gridded inventory of US anthropogenic methane emissions has a 0.1° × 0.1° spatial resolution, monthly temporal resolution, and detailed scale-dependent error characterization. The inventory is designed to be consistent with the 2016 US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Inventory of US Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Sinks (GHGI) for 2012.
The importance of this dataset and the work from Jacob's team at Harvard is that the CMS data shows large differences with the EDGAR v4.2 global gridded inventory commonly used as a priori estimate in inversions of atmospheric methane observations, and provides an improved basis for inversion of atmospheric methane observations to estimate US methane emissions.
Maryland Department of Natural Resources
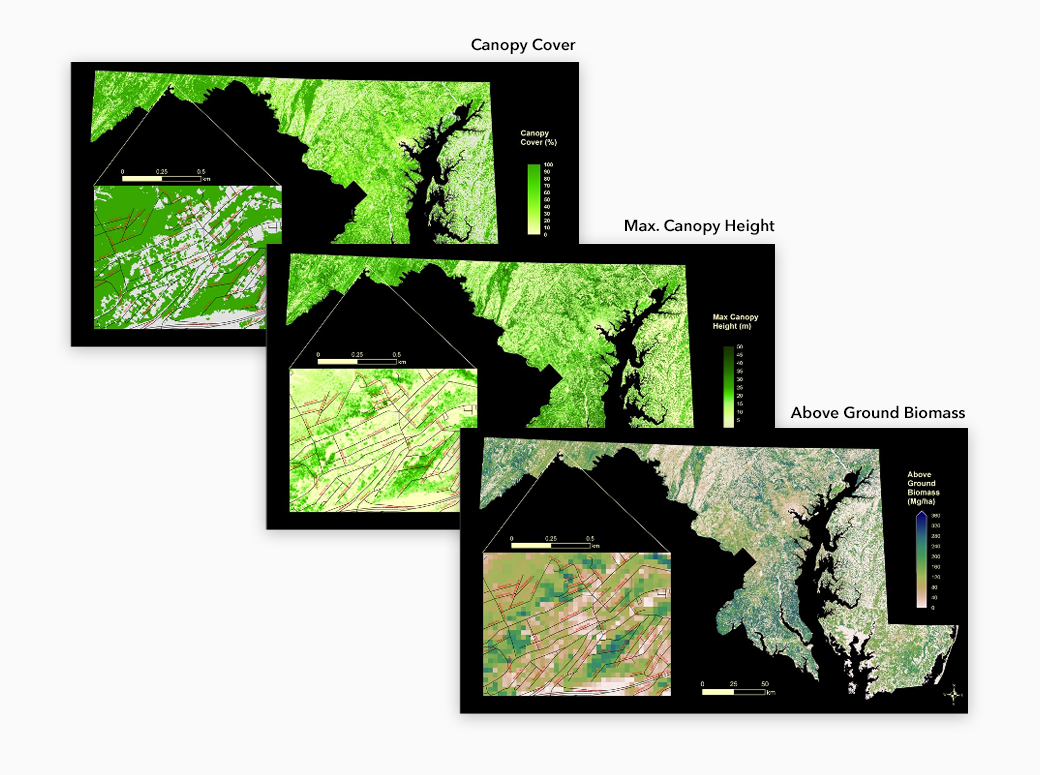
The Maryland Department of Natural Resources has been engaging for several years with CMS-funded scientists and leadership to use high-resolution forest carbon monitoring and modeling products to inform the state’s forestry sector, as well as to achieve their climate mitigation goals.
The Maryland state agency has engaged with CMS Science Team Lead and Principal Investigator, George Hurtt, and his team at the University of Maryland to use products such as Lidar-derived above ground biomass, canopy height and canopy cover maps, and carbon sequestration maps to inform the state’s forestry and sequestration sector, and to support forest preservation efforts in the state. Some of the science questions the project continues to address includes what is the potential of forests in the state to gain carbon in the future, and how long will that take.
RMI (formerly Rocky Mountain Institute)
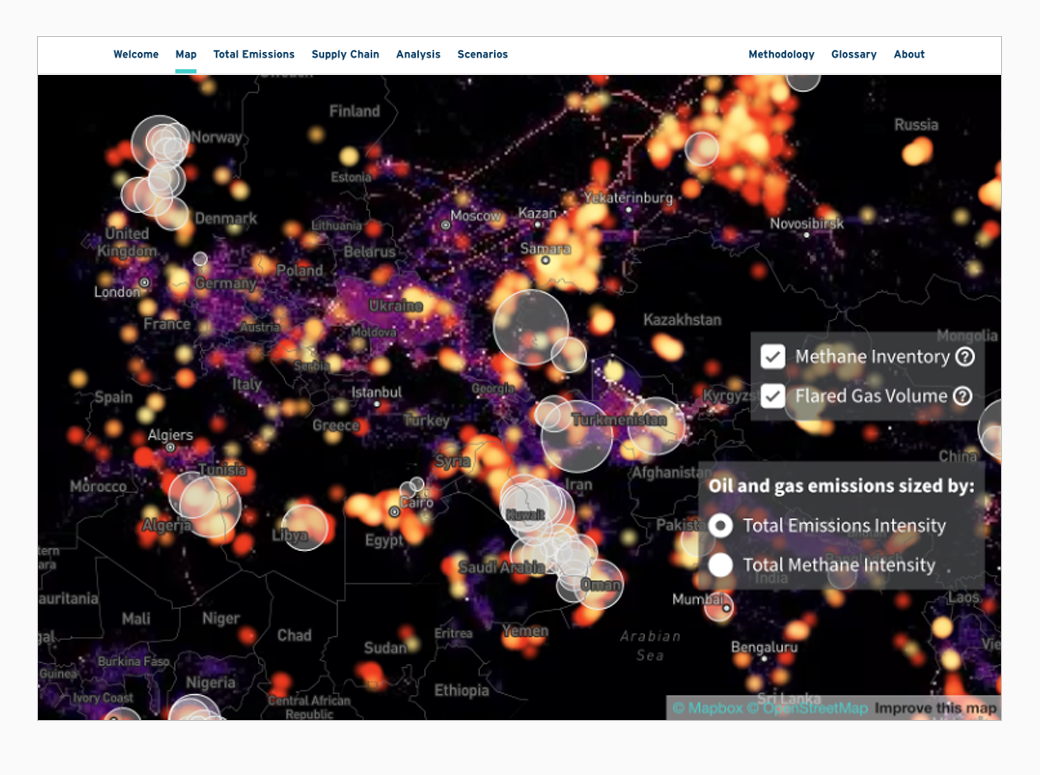
RMI has been working with several CMS projects and scientists to integrate a diverse set of CMS products into their Oil Climate Index plus Gas (OCI+) web tool, which assesses emissions from half of the world’s oil and gas supplies with unparalleled transparency. The OCI+ reveals differences between individual resources and provides important climate intelligence that operators, policymakers, investors, and civil society need to immediately reduce emissions.
The web tool has integrated datasets from CMS-funded projects led by Chris Elvidge, Daniel Jacob, and Riley Duren, amongst others, using data products such as the "Global Gas Flare Survey by Infrared Imagery, VIIRS Nightfire, 2012-2019", and the "Global Inventory of Methane Emissions from Fuel Explotation." The OCI+ webtool is being used for decision-making by stakeholders from all sectors, including the International Energy Agency (IEA), Aramco, Shell, Munich Re, the Norwegian Government, California Air Resources Board, amongst others.